BLD Insights
Boronic Acids & Bpins - First and Foremost!
15 August 2022
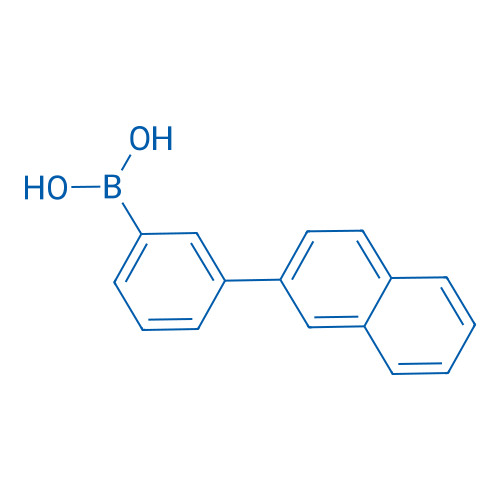
(3-(Naphthalen-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid
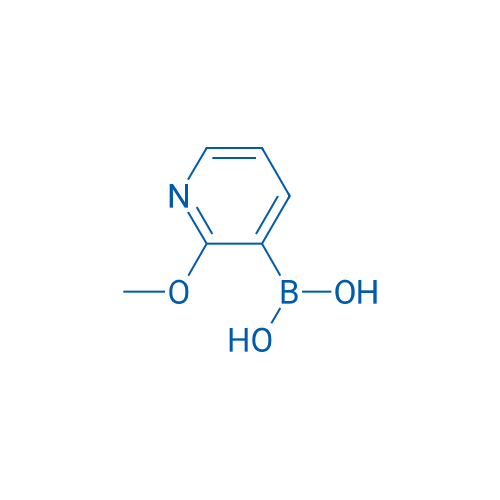
2-Methoxy-3-pyridineboronic acid
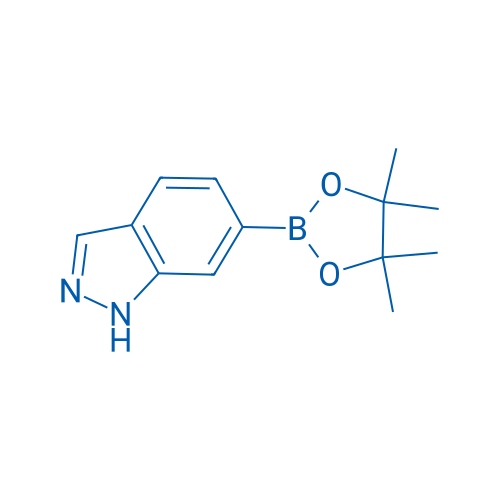
6-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-1H-indazole
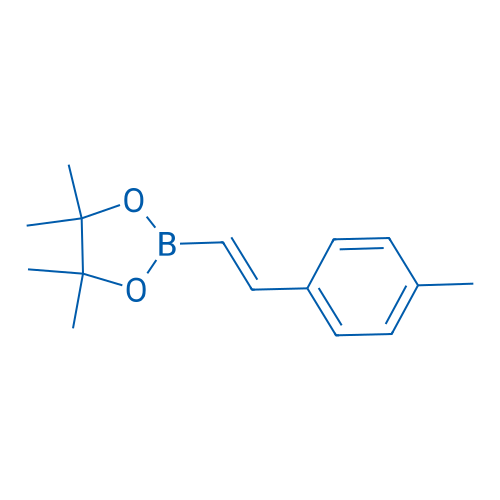
(E)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(4-methylstyryl)-1,3,2-dioxaborolane
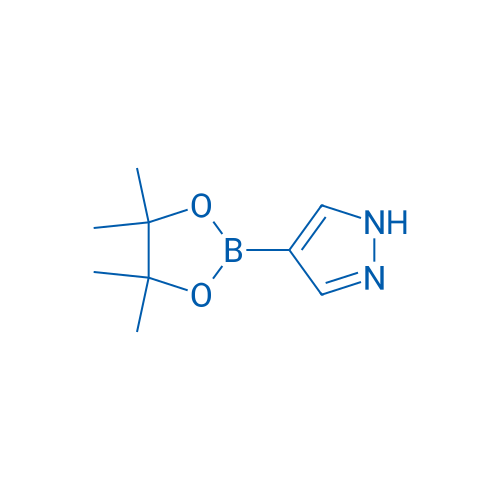
4-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-1H-pyrazole
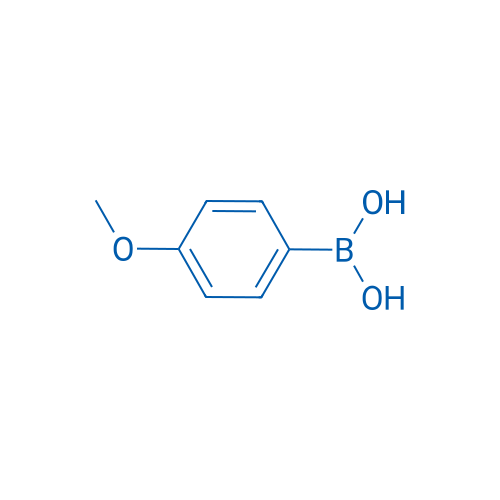
4-Methoxyphenylboronic acid
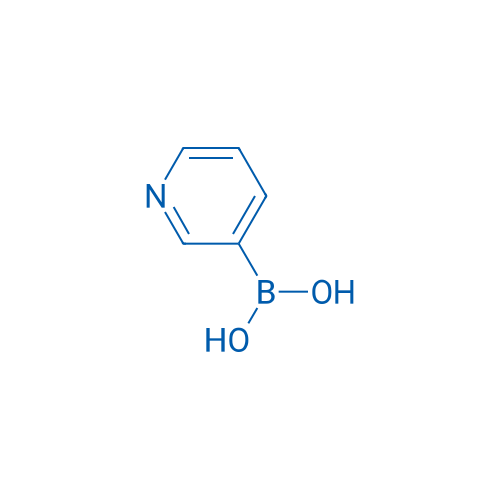
Pyridin-3-ylboronic acid
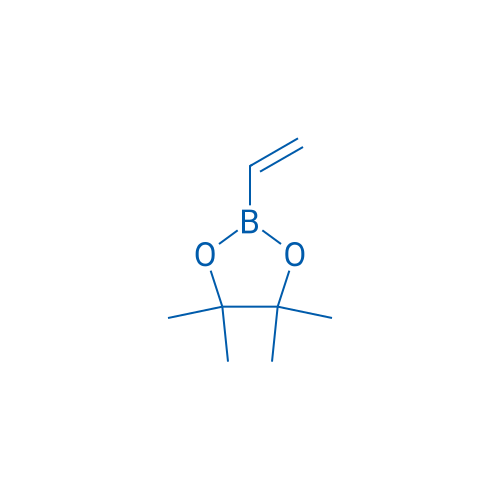
Pinacol vinylboronate
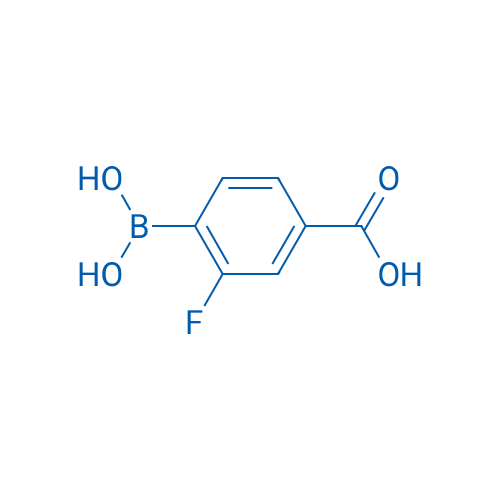
4-Borono-3-fluorobenzoic acid
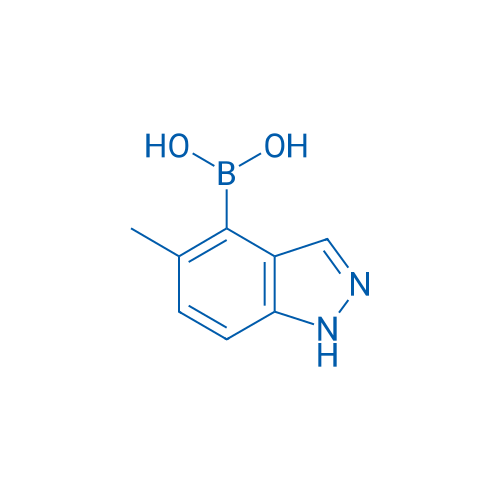
(5-Methyl-1H-indazol-4-yl)boronic acid

(3-(Naphthalen-2-yl)phenyl)boronic acid

2-Methoxy-3-pyridineboronic acid

6-(4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-1H-indazole

(E)-4,4,5,5-Tetramethyl-2-(4-methylstyryl)-1,3,2-dioxaborolane
A variety of organboron compounds can be used in the Suzuki-Miyaura reaction, of which boric acid is more generally applied because of its simplicity of synthesis, stability to water and air, and easy crystallization. The boron-containing by-products generated by organic boron reaction are soluble in water and non-toxic, which makes the reaction convenient and practical, and can be used for large-scale industrial synthesis.

However, boric acid always exists in the form of mixture, which is sensitive to some conditions and prone to side reactions of self-coupling. Organobpins are stable towards air and allow normal work up including chromatographic purification. Moreover, they may serve as coupling partners in the Suzuki Coupling and similar reactions without prior hydrolysis. Miyaura Borylation reaction enables the synthesis of Bpins by cross-coupling or C-H activation reactions with B2pin2, which provides plenty of useful building blocks.

Boric Acids and Bpins are the widest used organoborons and play key roles in Suzuki-Miyaura reaction.